In today’s business, capital is generated not by those who work harder, but by those who use available resources more wisely. This strategy, also called “resource leverage,” fundamentally changes the rules of the game. Here are some facts to consider:
- Uber's empire is valued at over $150 billion, but the company doesn't own a single car;
- Airbnb's market capitalization reached $75 billion without owning any hotels;
- Meta has become one of the most valuable brands in the world using content created directly by social media users;
- Banks increase their assets by operating with other people's money, not their own.
What conclusion can be drawn from this? It was clearly formulated in the company EYAccording to their data, businesses that have mastered the concept of “using other people's resources” increase profits by an average of 4% annually.
If we analyze successful business strategies, we can distinguish four main models of resource leverage.
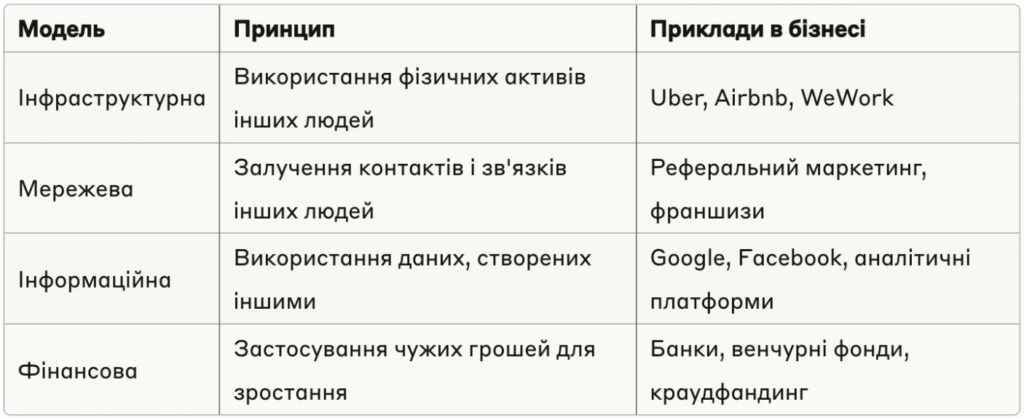
Ukrainian champions “resource leverage“
The strategy of using third-party resources also works successfully in Ukrainian realities.
Monobank: a bank without a bank
Monobank is a brilliant example of resource leverage in Ukraine. This story began in 2017, when a group of former top managers of PrivatBank decided to create a new banking brand… but without their own bank.
It would have been possible to invest hundreds of millions in creating an institution “from scratch,” but the Fintech Band team chose a different path:
- They used someone else's license – instead of going through the complicated procedure of obtaining a banking license, the team created a partnership with Universal Bank.
- We implemented a branchless model – the expensive branch network was replaced with a mobile app and card delivery.
- Initial investments were minimized - the launch of the project is estimated at $9 million, which is negligible compared to the launch of a traditional bank.
- They use third-party infrastructure – to issue cards, the team organized a network of partner points throughout Ukraine.
The result: in the first 2.5 years, monobank attracted 2 million customers, and now serves over 9 million users. The cost of attracting one customer at the beginning of the bank's formation turned out to be less than $5, while traditional banks spent $100-200 on it.
“Nova Poshta”: maximum return on minimal investment
Nova Poshta is another example of a Ukrainian business where the team started with minimal resources but managed to create a company of national scale.
Several resource leverage strategies from its founders Vyacheslav Klymov and Volodymyr Popereshnyuk:
- Minimal initial investment – in 2001, they launched the business with just $7,000 – an amount that was enough to rent small offices in three cities and an old Slavuta for transportation.
- Using other people's contacts instead of advertising - we started with "telephone business" - we called potential clients using the existing business network.
- Franchise scaling model – for rapid expansion without large capital investments, the company implemented a franchise model, which allowed it to increase the network to over 8,700 branches, using investments from partners.
- Crisis as an opportunity – in 2008, when most companies were “hiding” due to the financial crisis, Nova Poshta went all-in, actively expanding its network, and in two years increased the number of branches from 80 to 140.
- Human resource leverage – the company created a “Corporate University,” which encouraged ordinary workers to quickly climb the career ladder (as in the case of Yevhen Tafiychuk, who worked his way from a loader to an operations director).
Today, Nova Poshta is not just a company, but a full-fledged ecosystem with various services, including international transportation, logistics services, and financial transactions.
The old "Slavuta", from which the business began, is engraved on a pedestal near the Kyiv Innovation Terminal as a symbol of the fact that to start a big business, it is not necessary to have large resources - it is enough to skillfully use the ones you have.
Psychological barriers to resource leverage
Why don't all entrepreneurs use this strategy? Research has identified four key psychological barriers:
- “I have to control everything” – the fear of losing control forces many businessmen to focus only on their own resources, limiting the company's growth potential.
- “First – for yourself, then – for others” is a false belief that you must first achieve success on your own before attracting outside resources.
- “It doesn’t work in my industry” – the belief that the business is “special” and does not correlate with a leverage strategy.
- “I don’t know the right people” – limiting the social network to the boundaries of “my circle”, which reduces access to various resources.
A strategy for building relationships that multiply wealth
The use of resource leverage is associated with the development of a network of contacts:
- Determine your unique value – how you can be useful to potential partners (experience, knowledge, contacts).
- Create a resource map – identify 10 key resources that can accelerate your growth and the individuals who have access to them.
- Take the first step – offer help and value to others before asking for anything in return.
- Invest in relationships – stay in touch and help your contacts without expecting immediate benefits.
- Create a system of exchange – establish clear “rules of the game” so that all parties benefit.
Five levels of resource leverage: from Ukraine to global business
Analyzing the success stories of monobank, Nova Poshta, and Rozetka, we can identify five levels of resource leverage that successful companies use. Each subsequent level opens up greater opportunities for growth.
Level 1 – use of available resourcesThe basic principle is to sell what you don't own: Rozetka sells goods that it doesn't produce, Nova Poshta started with one Slavuta and rented offices, Uber attracts cars from private drivers, and Airbnb rents out other people's apartments.
Level 2 – infrastructure useThe main principle is to build a business on existing infrastructure: monobank uses the banking license of Universal Bank, Rozetka developed as an online platform without its own retail network, and Nova Poshta uses franchise branches built by partners.
Level 3 – use of human resourcesThe main principle is to attract the knowledge, expertise and connections of other people: Nova Poshta attracts franchise partners not only to open branches, but also to attract customers in new regions, monobank uses viral marketing and customer recommendations, and Rozetka has attracted tens of thousands of sellers to the partnership who bring their customers.
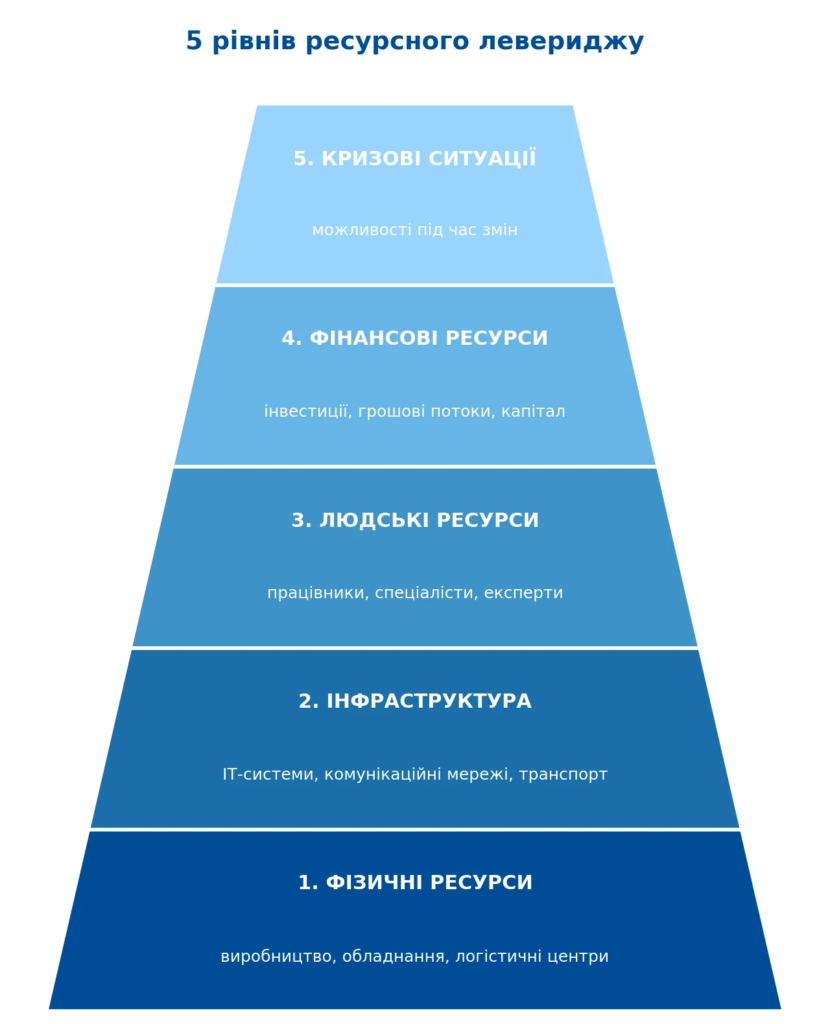
Level 4 – use of financial resourcesThe main principle is to attract external investments for growth: Rozetka raised funds from the Horizon Capital fund to accelerate development, Nova Poshta uses investments from franchise partners, and monobank used initial investments from Serhiy Tigipko.
Level 5 – use of crisis situations. The main principle: turn crises into opportunities: Rozetka increased purchases during the 2008-2009 crisis while competitors reduced them, Nova Poshta actively scaled up during the 2008 financial crisis, and monobank emerged after the banking crisis, managing to offer an alternative to traditional banks.
These five levels are not just theory, but real strategies used by the most successful companies in Ukraine and the world. To maximize business efficiency, strive to gradually master all levels of resource leverage.
Digital revolution: new opportunities for resource leverage
Modern digital technologies open up unprecedented opportunities for using “other people’s resources”:
- The API economy allows you to integrate the functionality of other companies into your own products.
- Cloud technologies provide access to computing power without capital expenditure.
- Freelance platforms help attract talent from around the world without formal hiring.
- Social networks make it easier to find and connect with potential partners.
Companies that actively use these capabilities demonstrate higher performance on the 40%.
Time to change your mindset: practical steps
Using resource leverage strategies is not just theory, but a real way to create a successful business in today's environment. Here are some practical steps to get you started:
Step 1 – rethink your resource needs.
Ask yourself, “Do I really need to own all the resources for my business?” If you’re planning to open a restaurant, is it necessary to buy a space? It might be better to rent or use a dark kitchen model (a kitchen purely for delivery).
Step 2 – identify the key assets of your business.
Successful companies focus on their unique advantages, and everything else is obtained through partnerships: monobank focused on customer experience and mobile application, Rozetka - on online platform and marketing; Nova Poshta - on logistics and service.
Step 3 – look for partners instead of suppliers.
Instead of just buying goods or services, look for strategic partners:
- offer the supplier a profit-sharing model instead of a fixed fee;
- attract partners who are able to invest in your joint project;
- Consider a franchise model for rapid expansion.
Step 4 – use digital platforms.
Digital tools allow you to scale your business with minimal costs:
- use existing marketplaces instead of creating your own online store;
- use cloud services instead of purchasing your own servers;
- Hire freelancers instead of expanding your staff.
Step 5 – act when others hesitate.
Crisis periods are the best time for growth:
- prepare reserve capital in advance for investments during economic downturns;
- Analyze competitors' reactions to the crisis – adapt successful solutions and take advantage of miscalculations.
- look for opportunities to purchase assets at discounted prices.
Start today. Analyze your business (or business idea) and identify three resources that you can gain through partnerships instead of direct investment. Develop an action plan to attract these resources over the next 3-6 months.
The stories of the formation of monobank, Nova Poshta, and Rozetka prove that in Ukraine you can create a multi-million dollar business, even if you don't have a large starting capital. The main thing is to use the available resources and opportunities correctly.
